What is a digital potentiometer?
 A digital potentiometer (also known as digital resistor) has the same function as a normal potentiometer but instead of mechanical action it uses digital signals and switches. This is done by making use of a ‘resistor ladder’, a string of small resistors in series. At every step of the ladder, an electronic switch is present. Only one switch is closed at the same time and in this way the closed switch determines the ‘wiper’ position and the resistance ratio. The amount of steps in the ladder determines the resolution of the digital pot. The diagram below shows the working principle of a digital potentiometer with 64 steps. Digital resistors can be controlled by using simple up/down signals or by serial protocols such as I²C or SPI.
A digital potentiometer (also known as digital resistor) has the same function as a normal potentiometer but instead of mechanical action it uses digital signals and switches. This is done by making use of a ‘resistor ladder’, a string of small resistors in series. At every step of the ladder, an electronic switch is present. Only one switch is closed at the same time and in this way the closed switch determines the ‘wiper’ position and the resistance ratio. The amount of steps in the ladder determines the resolution of the digital pot. The diagram below shows the working principle of a digital potentiometer with 64 steps. Digital resistors can be controlled by using simple up/down signals or by serial protocols such as I²C or SPI.
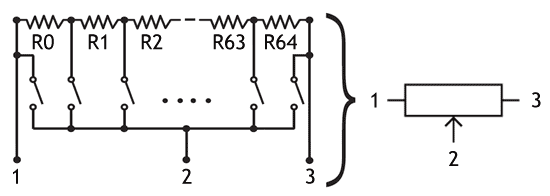
Digital potentiometer definition
A digital potentiometer is a variable resistor which is controlled by digital signals instead of by mechanical movement.
Properties of digital potentiometers
Digital potentiometers are integrated circuit (ICs), some variants have a nonvolatile memory (EEPROM) which remembers the ‘wiper’ position. When there is no on-board memory, the initial position of the wiper is often the middle position. Because of their relatively small size compared to conventional potentiometers, multiple potentiometers can be packed on a chip and ICs with up to 6 channels are available.
The amount of steps available determines the resolution of the digital potentiometer. The following table lists common step values available, including the bit count:
| Number of steps | ||||||
| Bits | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Steps | 32 | 64 | 128 | 256 | 512 | 1024 |
Digital resistors are available in a range of values, but 10 kΩ is the most used. Other common values are 5, 50 and 100 kΩ. The standard tolerance is 20% but nowadays digital potentiometers with a tolerance down to 1% are available.
Something to take into account when you start working with digital potentiometers is the fact that most of them are rated at 5V (to power the logic circuits). This can make it a bit tricky to use them as a direct replacement for conventional potentiometers.
Applications
Digital pots can be used in any application where normally a trimming potentiometer or preset-resistor is used. The big advantage of them is that they can be controlled in closed loop. When used for tuning, re-calibration can be done by a micro-controller at defined intervals. They are used in in for example brightness and contrast control of monitors, gain control or Wheatstone bridges and even digital-analog converters. The image below shows an example application of a digipot used for volume control. The potentiometer can be controlled via up/down signals, via buttons or a rotary encoder.
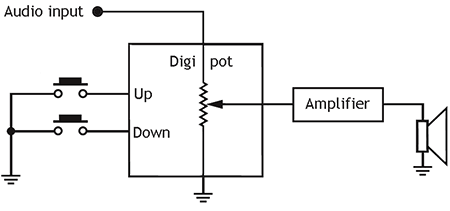
Digital potentiometer used for a volume control application