- Network Sites:
-
 EEPower Day is a free 1-day virtual conference. Learn More
EEPower Day is a free 1-day virtual conference. Learn More
Carbon film resistors are a type of fixed value resistor. They are constructed out of a ceramic carrier with a thin pure carbon film around it. This carbon film functions as the resistive material.
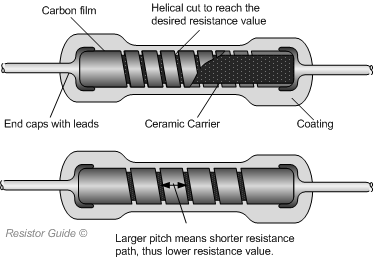 Construction of a carbon film resistor
Construction of a carbon film resistor
Carbon film resistors are a significant improvement on carbon composition resistors. However, in comparison to metal film and metal oxide film, the commercially available resistance range is limited. Metal and oxide film are not more expensive to produce and have overall better properties.
This type of resistor is widely used in electronics. Therefore it is important to note that the small resistors have a capacitance of approximately 0.5 pF. Also, self-induction is around 0.01 μH for uncut resistors and up to several μH for spiral cut resistors. These resistors are available in values between 1 Ω – 10,000 MΩ and have power ratings of 1/16, 1/8, 1/4, 1/2, 1, or 2 W.
The typical uses for carbon film resistors are in high voltage and high temperature applications. Operating voltages up to 15 kV with a nominal temperature of 350 °C are feasible for carbon film resistors.. Example uses include high voltage power supplies, radars, x-rays, and lasers.
Carbon film resistors are made with a deposition process. At high temperature and under a high pressure, a ceramic carrier is held in hydrocarbon gas. The gas (methane or benzene) is cracked at a temperature of 1000 °C. The crystaline carbon is pyrolytically deposited on the ceramic substrate. Because of the precise distribution of the pure graphite without binding, these carbon resistors have a low noise. The desired resistance value can be obtained by choosing the right layer thickness, and by cutting a spiral shape in the carbon layer. The helical cut in the film increases the length of the current path. By decreasing the pitch of the helix, the length of the resistive path increases, and therewith the resistance value increases. Furthermore, by fine tuning the cutting of the spiral, the resistor can have a higher accuracy of resistance value. Typical tolerance values for carbon film resistors are 2, 5, 10, and 20%.
Because of the use of pure carbon, the carbon film resistor has a higher negative temperature coefficient than carbon composition. The resistive temperature coefficient lies between 2.5×10-4 Ω/°C and -8×10-4 Ω/°C. Also, this type of resistor is protected against chemical influences with a silicone coating.