- Network Sites:
-
 EEPower Day is a free 1-day virtual conference. Learn More
EEPower Day is a free 1-day virtual conference. Learn More
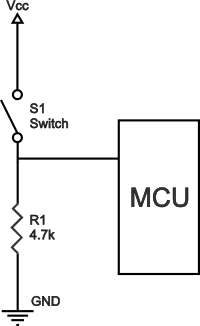
Pull-up resistors are resistors used in logic circuits to ensure a well-defined logical level at a pin under all conditions. As a reminder, digital logic circuits have three logic states: high, low and floating (or high impedance). The high-impedance state occurs when the pin is not pulled to a high or low logic level, but is left “floating" instead. A good illustration of this is an unconnected input pin of a microcontroller. It is neither in a high or low logic state, and the microcontroller might unpredictably interpret the input value as either a logical high or logical low. Pull-up resistors are used to solve the dilemma for the microcontroller by pulling the value to a logical high state, as seen in the follow figure.
 Pull-up resistor circuit
Pull-up resistor circuit
Without the pull-up resistor, the MCU’s input would be floating when the switch is open and pulled down to a logical low only when the switch is closed.
Pull-up resistors are not a special kind of resistors; they are simply fixed-value resistors connected between the voltage supply (typically +5 V, +3.3 V, or +2.5 V) and the appropriate pin, which results in defining the input or output voltage in the absence of a driving signal. A typical pull-up resistor value is 4.7 kΩ, but can vary depending on the application, as will be discussed later in this article.
Pull-up resistors are resistors which are used to ensure that a wire is pulled to a high logical level in the absence of an input signal.
Pull-down resistors work in the same manner as pull-up resistors, except that they pull the pin to a logical low value. They are connected between ground and the appropriate pin on a device. An example of a pull-down resistor in a digital circuit can be seen in the following figure.
 Pull-down resistor
Pull-down resistor
In this figure, a pushbutton switch is connected between the supply voltage and a microcontroller pin. In such a circuit, when the switch is closed, the microcontroller input is at a logical high value, but when the switch is open, the pull-down resistor pulls the input voltage down to ground (logical zero value), preventing an undefined state at the input. The pull-down resistor must have a larger resistance than the impedance of the logic circuit, or else it might be able to pull the voltage down by too much and the input voltage at the pin would remain at a constant logical low value – regardless of the switch position.
The appropriate value for the pull-up (or pull-down) resistor is limited by two factors. The first factor is power dissipation. If the resistance value is too low, a high current will flow through the pull-up resistor, heating the device and using up an unnecessary amount of power when the switch is closed. This condition is called a strong pull-up and is avoided when low power consumption is a requirement. The second factor is the pin voltage when the switch is open. If the pull-up resistance value is too high, combined with a large leakage current of the input pin, the input voltage can become insufficient when the switch is open. This condition is called having a weak pull-up. The actual value of the pull-up’s resistance depends on the impedance of the input pin, which is closely related to the pin’s leakage current.
A rule of thumb is to use a resistor that is at least 10 times smaller than the value of the input pin impedance. In bipolar logic families which operate at operating at 5 V, the typical pull-up resistor value is 1-5 kΩ. For switch and resistive sensor applications, the typical pull-up resistor value is 1-10 kΩ. If in doubt, a good starting point when using a switch is 4.7 kΩ. Some digital circuits, such as CMOS families, have a small input leakage current, allowing much higher resistance values, from around 10 kΩ up to 1 MΩ. The disadvantage when using a larger resistance value is that the input pin responds slowly to voltage changes. This is the result of the coupling between the pull-up resistor and the total pin and wire capacitance at the switching node which forms an RC circuit. The larger the product of R and C, the more time is needed for the capacitance to charge and discharge, and consequently the slower the circuit. In high-speed circuits, a large pull-up resistor can sometimes limit the speed at which the pin can reliably change state.
Pull-up and pull-down resistors are often used when interfacing a switch or some other input with a microcontroller or other digital gates. Most microcontrollers have built-in programmable pull-up and/or pull-down resistors, so fewer external components are needed. It is possible to interface a switch with these microcontrollers directly. Pull-up resistors are in general used more often than pull-down resistors, although some microcontroller families have both pull-up and pull-downs available.
They are often used to provide a controlled current flow into a resistive sensor prior to analog to digital conversion of the sensor output voltage signal.
Another application is the I2C protocol bus, where pull-up resistors are used to enable a single pin to act as an input or an output. When not connected to a bus, the pin floats in a high-impedance state.
Pull-down resistors are also used on outputs to provide a known output impedance.